Calculating Payroll Costs for Your Employees
Navigating the waters of payroll costs is more than just a routine task for businesses; it's a pivotal element in the grand scheme of financial...
9 min read
Enzo O'Hara Garza
:
Updated on September 24, 2024

As businesses continue to embrace remote work arrangements, navigating the complexities of remote employee payroll tax compliance has become a critical concern for employers. In this article, we'll investigate the nuances of payroll taxes and how they affect staff members working remotely in various areas, what are the most common mistakes you can make when managing your own payroll tax, and what you can do to stay on the IRS' good side.
Before we get started, you should know that...
Remote work has become a popular option for businesses of all sizes. In fact, according to the Pew Research Center,
Roughly three years after the COVID-19 pandemic upended U.S. workplaces, about a third (35%) of workers with jobs that can be done remotely are working from home all of the time.
While this number has dropped since 2022, this is roughly 4 times the pre-pandemic rate. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work, prompting companies to rapidly adapt their operations to accommodate a distributed workforce. While remote work offers numerous benefits to employees, such as flexibility and work-life balance, it's important to also consider the advantages it brings to employers.
Here's are the benefits employer's can expect when switching from IRL work to remote work:
One of the most significant benefits of remote work for employers is the potential for cost savings. Without the need for a large, centralized office, companies can save on expenses such as rent, utilities, office equipment, and maintenance.
Additionally, businesses can also save on ancillary costs, like commuter benefits and office perks. By reducing overhead costs, employers can allocate their resources more effectively and reinvest in other areas of the business.
When employers embrace remote work, they can tap into a much larger talent pool than those restricted to a specific geographic location. Companies can recruit from anywhere in the world, bringing in talented individuals with diverse skills, backgrounds, and perspectives. This diversity can foster creativity and innovation, ultimately strengthening the business's competitive edge.
Flexible work arrangements, such as remote work, have been shown to increase employee satisfaction and retention. By offering employees the opportunity to work remotely, employers can create a more supportive and appealing work environment. This not only helps attract top talent but also reduces turnover rates and the associated costs of recruiting, hiring, and training new employees.
Contrary to the outdated belief that remote workers are less productive, studies have shown that remote employees often demonstrate higher levels of productivity. The ability to work in a comfortable, distraction-free environment can lead to greater focus and efficiency. Additionally, remote work eliminates the time-consuming and often stressful daily commute, allowing employees to dedicate more time and energy to their tasks.
Remote work capabilities can provide businesses with greater resilience in the face of unforeseen challenges or emergencies. By enabling employees to work remotely, companies can maintain operations even when their physical office is inaccessible due to natural disasters, pandemics, or other disruptions. This added layer of business continuity can help ensure that a company's operations remain stable, regardless of external circumstances.
Remote work can contribute to an organization's corporate social responsibility and environmental sustainability efforts. By reducing the number of employees commuting to a physical office, companies can significantly decrease their carbon footprint. Moreover, with fewer people in the office, businesses can also reduce energy consumption, waste production, and other environmental impacts.
Remote work offers numerous benefits to employers, making it an increasingly attractive option for businesses across various industries. By embracing remote work, employers can enjoy cost savings, access a larger talent pool, improve employee retention, boost productivity, enhance business continuity, and contribute to environmental sustainability. As the future of work continues to evolve, adopting remote work arrangements may be an essential strategy for staying competitive and fostering long-term success.
So, you're on board with remote work, but you're worried about how this might affect how you manage payroll taxes? You've come to the right place. It is essential for employers to understand their payroll tax obligations for remote employees
Payroll taxes are taxes that are taken out of an employee's paycheck and paid by the employer to the government. These taxes are used to fund various programs such as Social Security and Medicare.
As a business owner, it's important to understand payroll taxes because you are responsible for withholding them from your employees' paychecks and paying them to the government. You must also keep accurate records of these taxes and file the appropriate forms with the government and if you don't, managing an audit later will be a giant headache.
Federal Income Tax: Withheld according to IRS guidelines based on an employee's W-4 form submission
Social Security & Medicare (FICA) Taxes: A fixed percentage withheld from employee wages, with employers contributing an equal amount
State Income Tax: Withheld according to individual state guidelines (not applicable in all states)
Local Taxes: Additional taxes that may be imposed by cities or counties on employees working within their jurisdiction
Unemployment Insurance Taxes: Paid by the employer at both federal and state levels to fund unemployment benefits for workers who lose their jobs through no fault of their own
To calculate payroll taxes, employers must first determine the appropriate withholding rates based on information provided by employees on their W-4 forms. Next, they need to apply these rates to each employee's gross pay while considering any pre-tax deductions such as retirement contributions or health insurance premiums. Finally, employers are responsible for remitting withheld amounts along with any additional required payments like FICA tax matching and unemployment insurance contributions.
Need help calculating payroll taxes in a pinch?
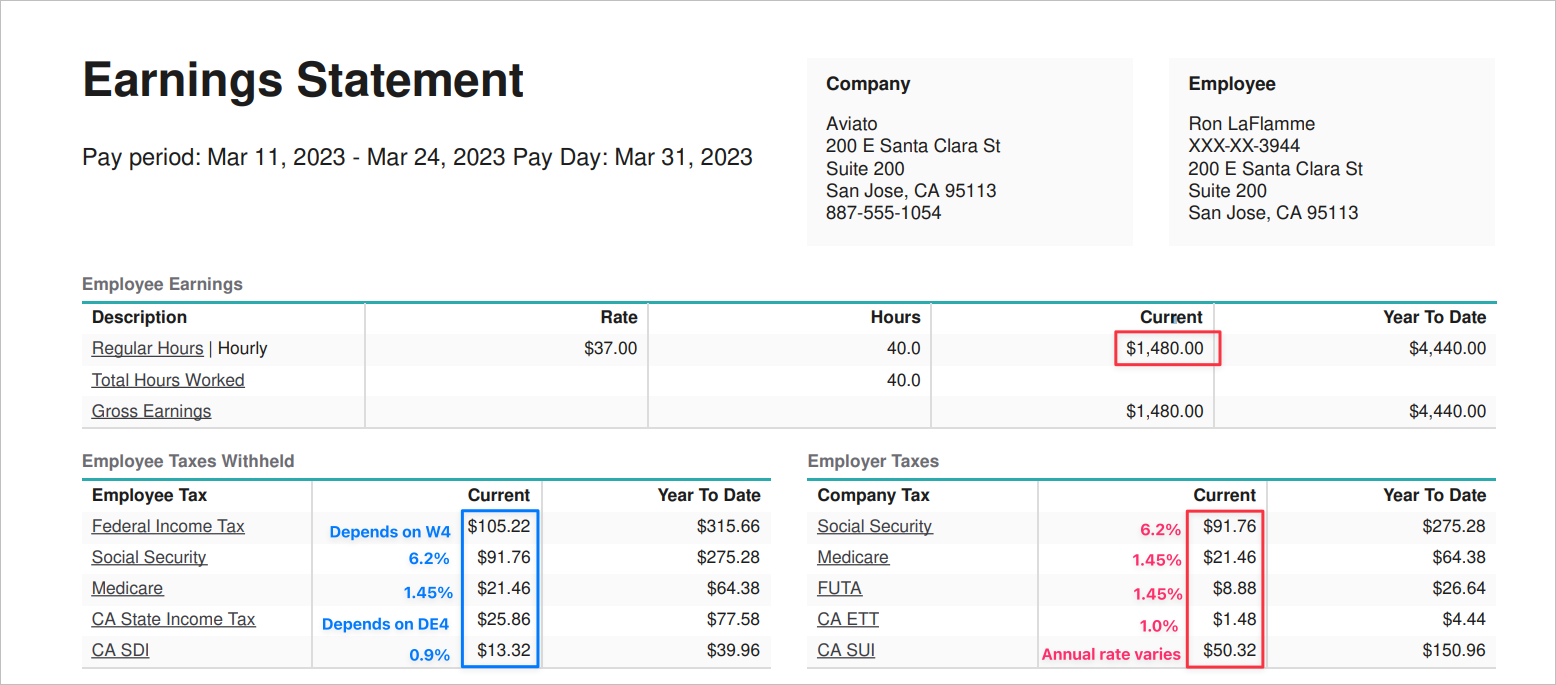
Here is an example of a paystub for a fictitious person. You can see that their Gross Wages are $1,480 for this pay period.
The employee's portion of payroll taxes are:
Federal Income Tax (FIT) - This is determined by the employee's W4 form.
Social Security - 6.2% - Up to the taxable maximum of $160,200 (in 2023), and is the same for the employer and employee.
Medicare - 1.45% - This is the same for the employer and the employee.
California (CA) State Income Tax (SIT) - This is determined by the state version of the W4 form, which varies by state. In this example, this person would fill out a DE4 form.
California State Disability Insurance (aka CA SDI) - This is paid for by the employee.
The federal taxes are consistent, while the state taxes depend on where the employee lives and performs their work.
The employer portion of payroll taxes are:
Social Security
Medicare
Federal Unemployment Tax (FUTA)
California (CA) Employment Training Tax (ETT) - This is paid for by the employer and provides funds to train employees in targeted industries.
California (CA) Unemployment Insurance (SUI) - This is paid for by the employer and pays benefits to people who are unemployed through no fault of their own. New employers are assigned a 3.4 percent UI rate for two to three years. After that, your contribution tax rate varies, depending in part on how much you’ve paid in UI benefits.
As you can see, no matter where a worker is situated within the US, employers must deduct Social Security and Medicare taxes from their employees' wages as mandated by federal regulations. However, businesses must also adhere to state-specific regulations, which may include withholding state income taxes or paying unemployment insurance contributions on behalf of your remote employees.
When it comes to remote employee payroll tax compliance, there are several common mistakes that employers often make. To ensure payroll tax compliance, it is essential to understand the common mistakes and how to prevent them.
One common mistake is failing to withhold or remit the correct amount of taxes from your employees' wages. This can lead to penalties and interest charges for underpayment or late payment of taxes owed by remote employees.
To avoid this issue:
Ensure you have accurate information about each employee's residency status, work location, and tax withholding preferences.
Make sure these changes are updated in your payroll software, as soon as they occur.
Stay up-to-date with changes in local, state, and federal regulations regarding remote employee payroll tax compliance.
Filing incorrect reports or making late payments can also result in costly fines for non-compliance with remote employee payroll tax laws.
To prevent these issues:
Create a schedule for filing required reports (such as quarterly filings) so you don't miss any deadlines (or use a payroll software to do this for you).
Audit your reporting process regularly to identify errors before they become problem
Respond to notices (or forward these notices to your accounting team as soon as they arrive). Waiting to take care of a notice can cost you, big time.
Maintaining accurate records is crucial for remote employee payroll tax compliance. Inaccurate bookkeeping can cause taxes to be either not enough or too much, which could result in fines and additional interest.
To ensure proper record-keeping implement a system for tracking payments made and withheld from employee wages (ahem.. payroll software) and regularly review your records for accuracy and completeness.
As regulations change frequently, it 's essential that you stay informed about updates related to remote employee payroll tax compliance. Failing to stay on top of changes could result in serious repercussions, including fines or other penalties.
To keep up-to-date subscribe to newsletters or alerts from relevant government agencies (such as the IRS) or join professional organizations where you can network with peers who may have insights into recent changes impacting remote employee payroll tax compliance
Lastly, many employers make the mistake of not seeking professional assistance when it comes to remote employee payroll tax compliance. This can lead to costly errors and missed opportunities for optimizing your processes.
To avoid this pitfall recognize when you need help - whether it's due to a lack of expertise, time constraints, or simply needing an external perspective. Reach out to professionals (like Accountingprose) who specialize in small business accounting and payroll services , ensuring that your company remains compliant with all relevant regulations while also streamlining operations .
Let's start with the IRS penalties you can expect if you fail to pay on time, pay the wrong amount, or pay incorrectly.
|
Number of Days Your Deposit is Late |
Amount of the Penalty |
|---|---|
|
1-5 calendar days |
2% of your unpaid deposit |
|
6-15 calendar days |
5% of your unpaid deposit |
|
More than 15 calendar days |
10% of the unpaid deposit |
|
More than 10 calendar days after the date of your first notice or letter (for example, CP220 Notice) |
15% of your unpaid deposit |
It's important to note that these penalties aren't tiered, meaning if your deposit is more than 15 calendar days late, they don’t add a 10% penalty to the earlier 2% and 5% late penalties. Instead, the entire amount would be subject to a 10% penalty.
What if you've also forgotten to file or have filed late?
|
Type of Penalty |
Interest |
|
Failure to File |
The Failure to File Penalty is 5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that a tax return is late. |
|
Failure to File > 60 days Late |
If your return was over 60 days late, the minimum Failure to File Penalty is $435 (for tax returns required to be filed in 2020, 2021 and 2022) or 100% of the tax required to be shown on the return, whichever is less. |
|
Failure to File and Pay |
If both a Failure to Pay and a Failure to File Penalty are applied in the same month, the Failure to File Penalty will be reduced by the amount of the Failure to Pay Penalty applied in that month. |
Additionally, you can expect to hit with interest on late filing penalties, and the rate depends on which type of penalty. The IRS has updated interest rates here, and as Q2 2023 range from 4% to 9%..
Each state will have their own fee structure and, using California as an example, you can expect to be charged a penalty of 15% plus interest on late payroll tax payments... This stuff really adds up!
Also, if you fail to pay and the IRS wants to collect, they may file a Notice of Federal Tax Lien which gives them the authority to deduct the funds from your bank account without prior authorization and may even attempt to withdraw funds from your personal account, if you are an authorized signer on the account. So, I guess the lesson here is... "Don't F with the IRS."
To ensure compliance with remote employee payroll tax obligations, consider implementing the following strategies:
Use payroll software like Gusto to automatically calculate payroll tax amounts, file forms, and remit payroll tax on time, every time.
As soon as you realize you have nexus, find out what accounts need to be set up. This can include state income tax withholding and unemployment insurance accounts.
Check with your CPA to see if hiring an employee in a new state will create additional business income tax liability and set up any business licenses that they recommend.
Update your workers' compensation policy to include the new state your team is in, so that they are covered.
Review and revise your employee handbook to include state-specific policies you've not had to include before.
Provide regular training sessions on company policies related to remote employment/payroll taxes so everyone understands their responsibilities clearly.
Hire an accounting team (shameless plug for Accountingprose) to handle all of this for you, so you never worry about missing a step.
It is critical for employers with a remote team to understand their responsibilities concerning payroll tax compliance. By automating processes, utilizing professional services and establishing clear policies and procedures, employers can ensure that they are meeting all of the necessary requirements for remote employee payroll taxes.
By understanding the payroll tax compliance obligations for employers with remote employees, utilizing strategies to ensure those obligations are met, and avoiding common mistakes in this area, businesses can rest assured that their remote employee payroll taxes are being managed correctly.
Let Accountingprose help you save time and money on remote employee payroll tax compliance. Our comprehensive services are designed to ensure your small business is compliant with all regulations while optimizing processes to be most efficient.

Navigating the waters of payroll costs is more than just a routine task for businesses; it's a pivotal element in the grand scheme of financial...
.png)
Gusto Payroll is a cloud-based payroll solution designed to simplify and streamline the payroll process for businesses. With a focus on automation,...

The task of maintaining payroll records might seem like a mundane detail, yet it stands as a cornerstone of sound financial and legal practice. For...